2: principles and techniques
Realistically, most likely failures, actions to those failures.
1, failures from the customer, FA, actions reliability analyses.
2. understadings of inherent reliability of a product or process and pinpoint potential areas for reliability improvement.
3. effects of design changes and corrections.
team, including reliability engineers, quality engineers, test engineers,
systems engineers or design engineers.
4 things: probability, intended function, a specified period of time, under stated conditions.
What is Reliability? reliability can be defined as the probability that an
item will continue to perform its intended function without failure for a
specified period of time under stated conditions.
Why is Reliability Important? What is the Difference Between Quality and
Reliability?
http://weibull.com/basics/reliability.htm
Reputation. A company's reputation is very closely related to the reliability
of its products. The more reliable a product is, the more likely the company is
to have a favorable reputation.
Chain of reputation: reliability is not a probability, one failure in critical
moment is not a probability
human psychological effect, 99 good things may have same impact as one bad thing
Competitive
quality time 0 good, sorting, good dies, pass functional tests
reliability, devices, HCI, mosfet, ILD, leakage time dependant
design, process, poorly manufactured. , even though the product design,
manufacturing process.
http://nutek-us.com/wp-doe.html
- Optimize product and process designs, study the effects of multiple factors (i.e.- variables, parameters, ingredients, etc.) on the performance, and solve production problems by objectively laying out the investigative experiments. (Overall application goals)
- Study Influence of individual factors on the performance and determine which factor has more influence, which ones have less. You can also find out which factor should have tighter tolerance and which tolerance should be relaxed.
DOE using Taguchi approach attempts to improve quality which is defined as the consistency of performance. This can be done by moving the mean performance to the target as well as by reducing variations around the target. The prime motivation behind the Taguchi experiment design technique is to achieve reduced variation (also known as ROBUST DESIGN).
Further, the experimental data will allow you determine:
- How you can determine which factor is causing most variations in the result
- How you can set up your process such that it is insensitive to the uncontrollable factors
- Which factors have more influence on the mean performance
- What you need to do to reduce performance variation around the target
- How you can adjust factors for a system whose response varies proportional to signal factor (Dynamic response)
Introduced by R. A. Fisher in England in the 1920's
The Taguchi Approach , Dr. Genechi Taguchi DOE techniques in the late 1940's



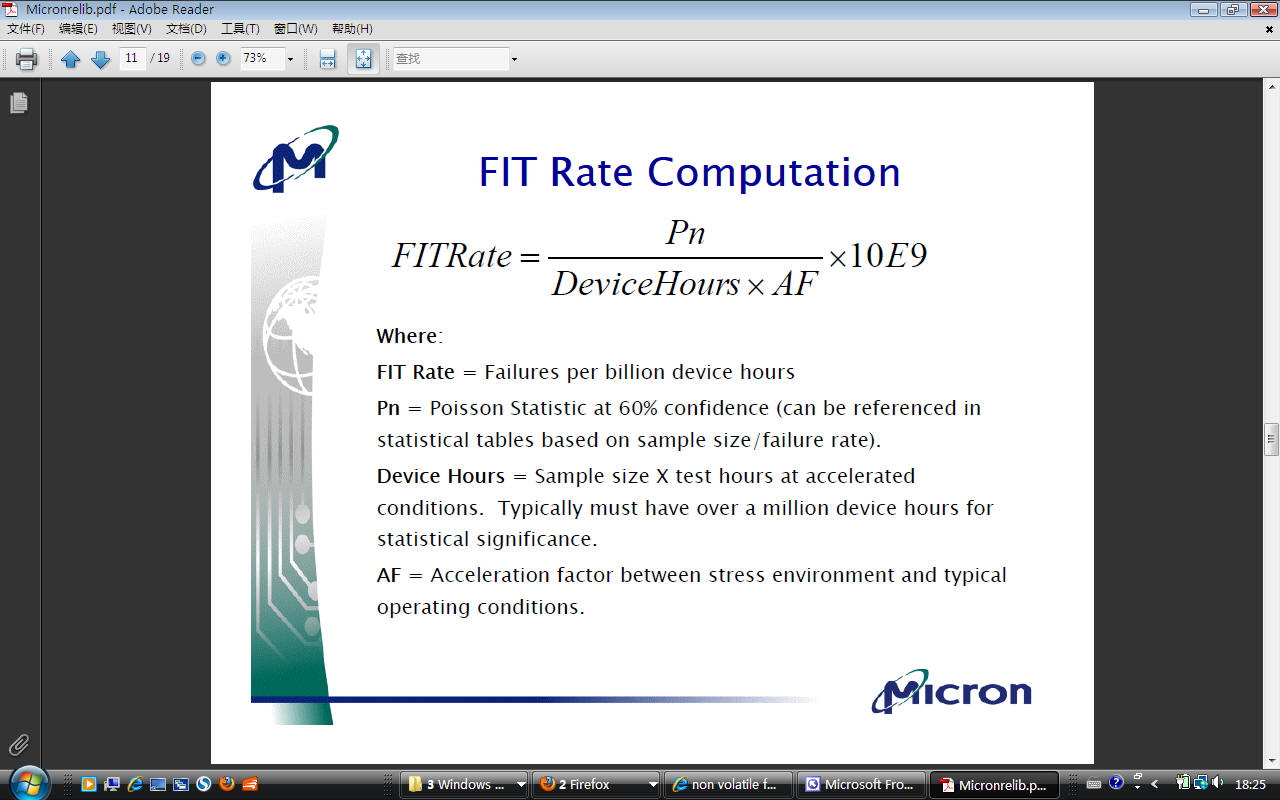
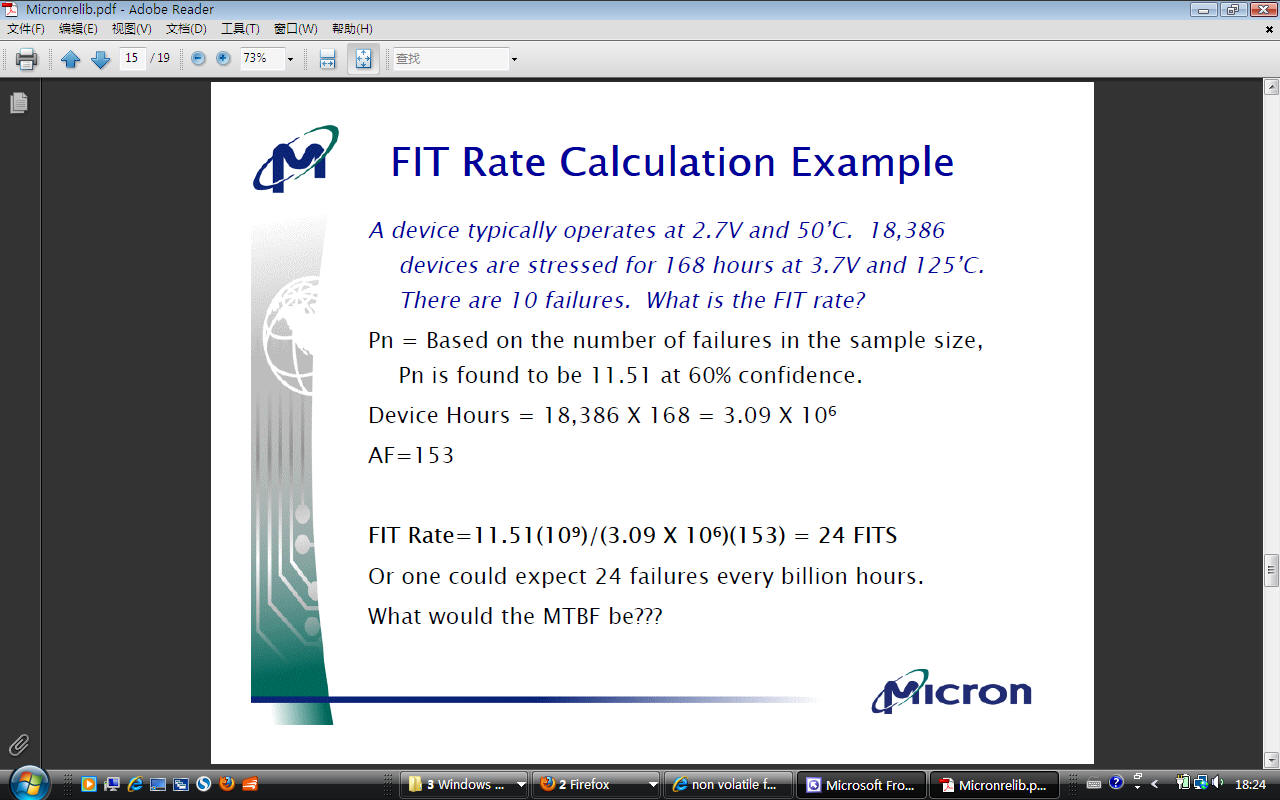

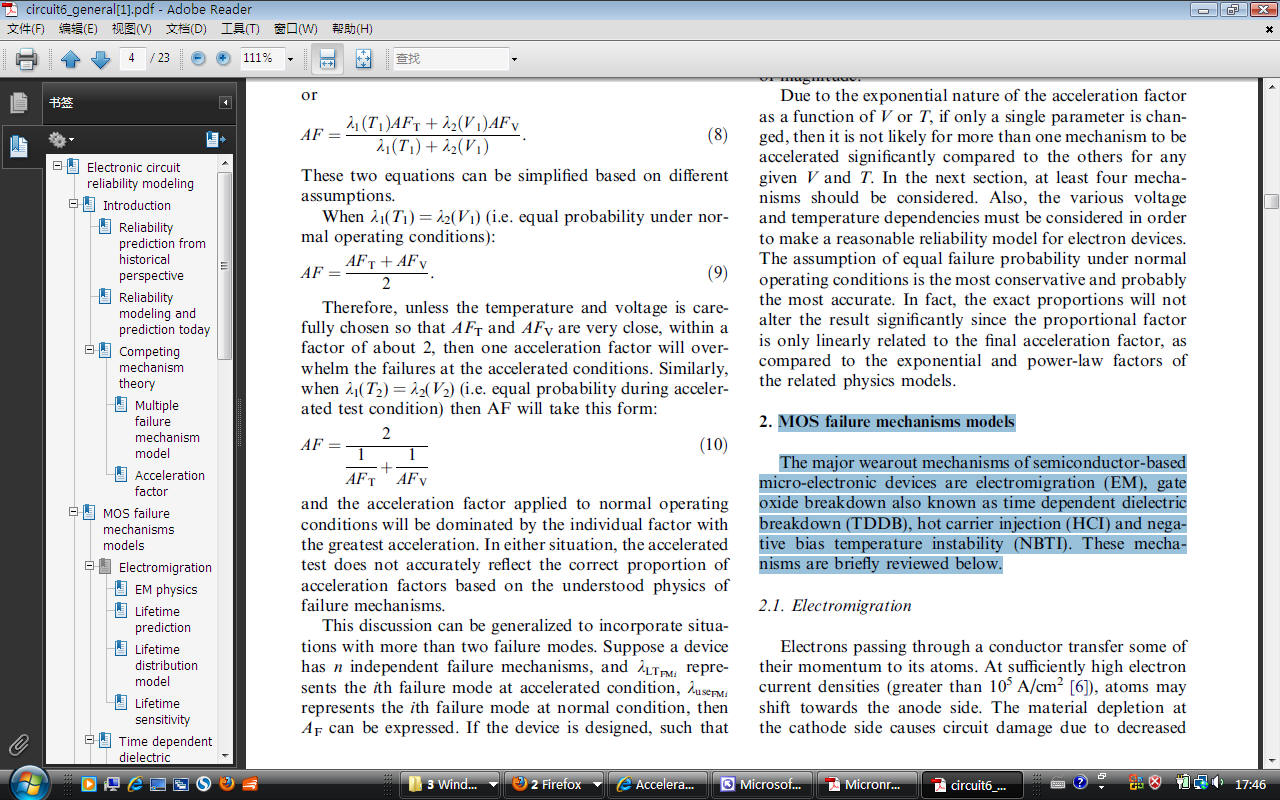

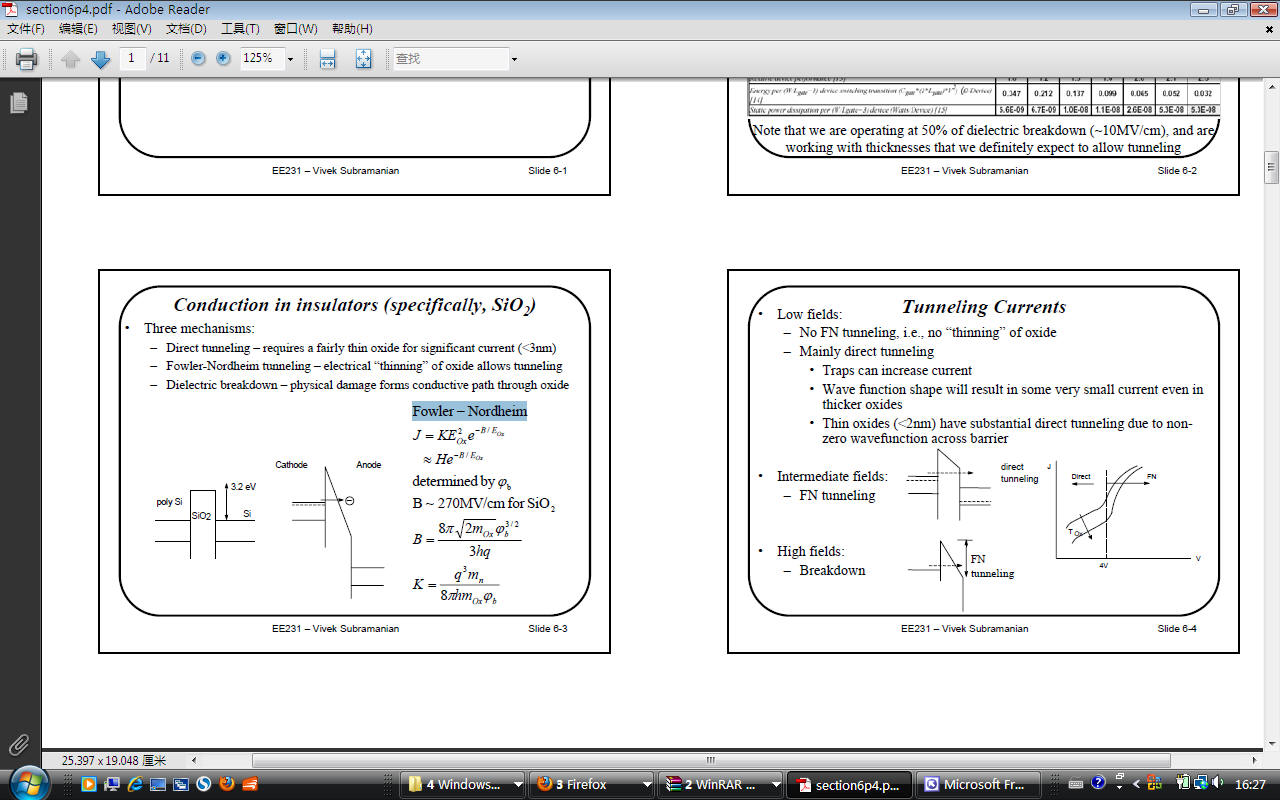
Breakdown field ~ 8 MV/cm for thick oxides and increases > 10 MV/cm for thinner oxides.

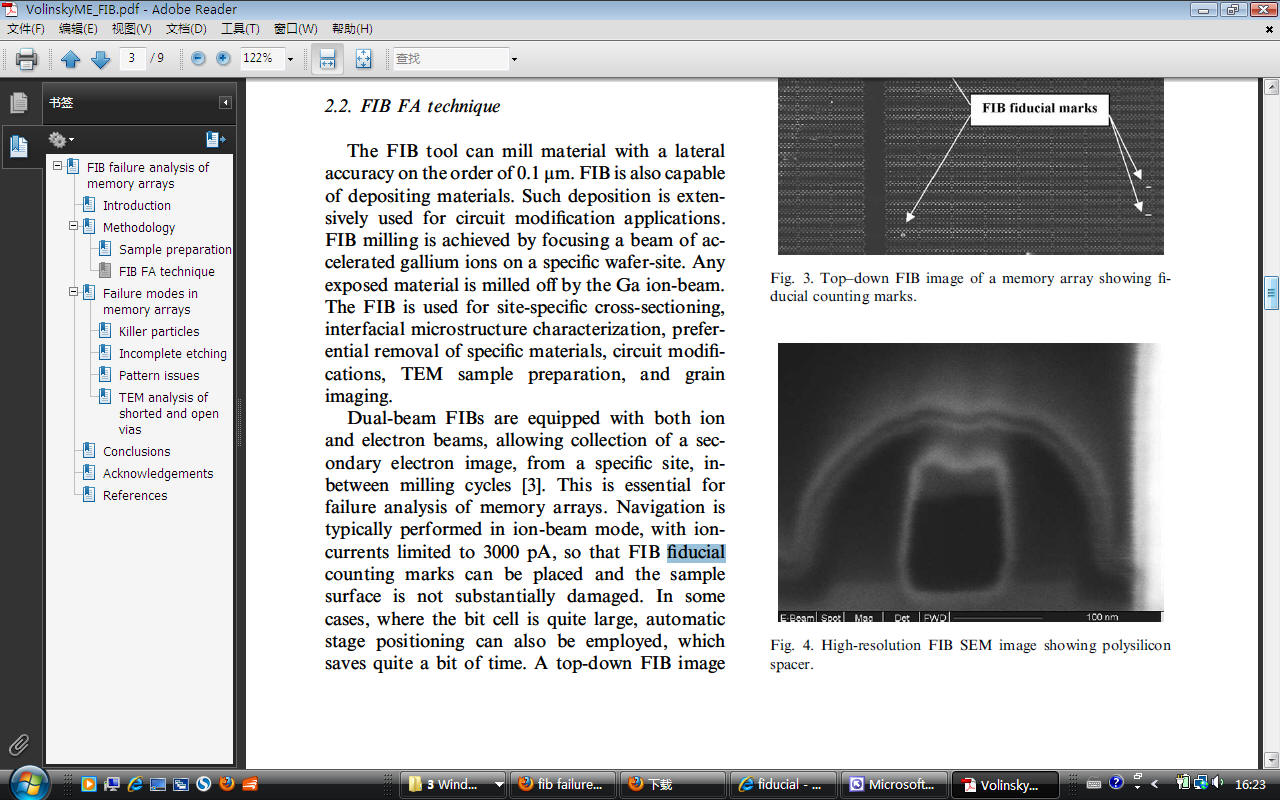
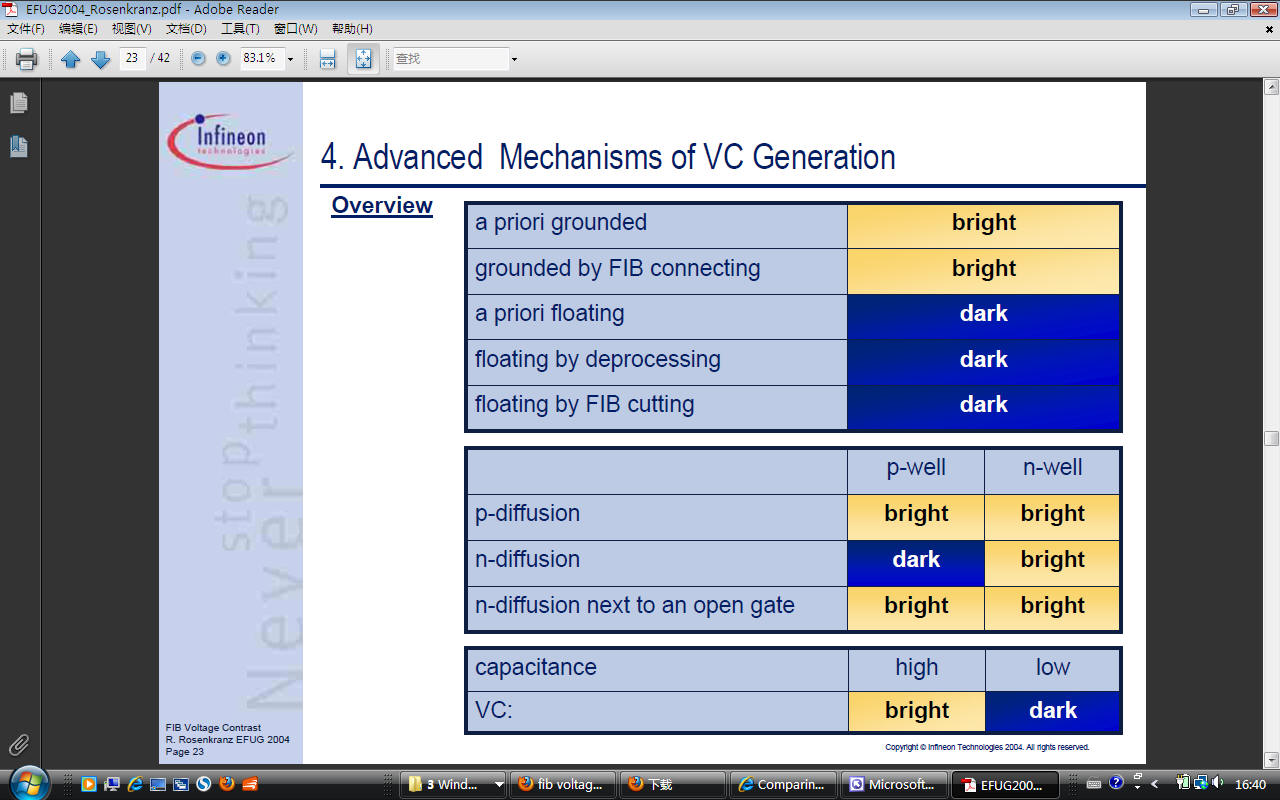
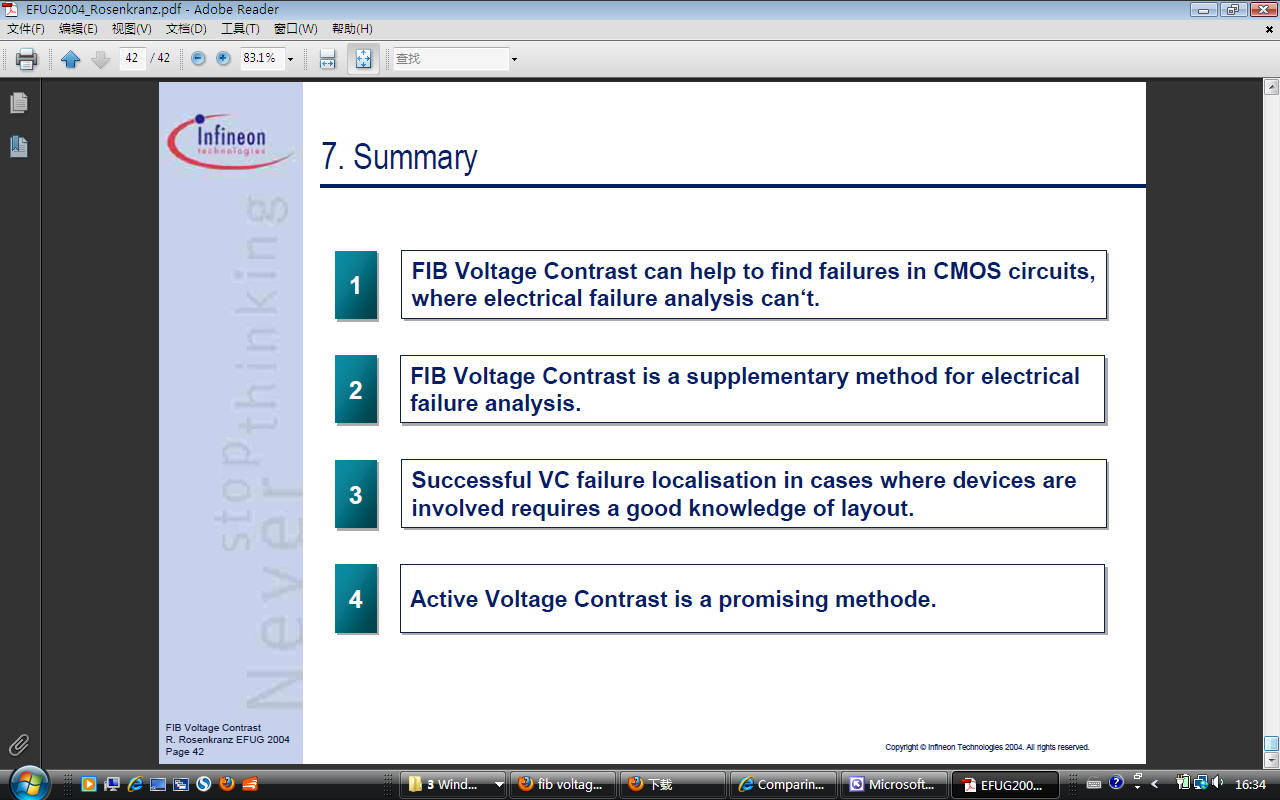
FA FIB, voltage contrast
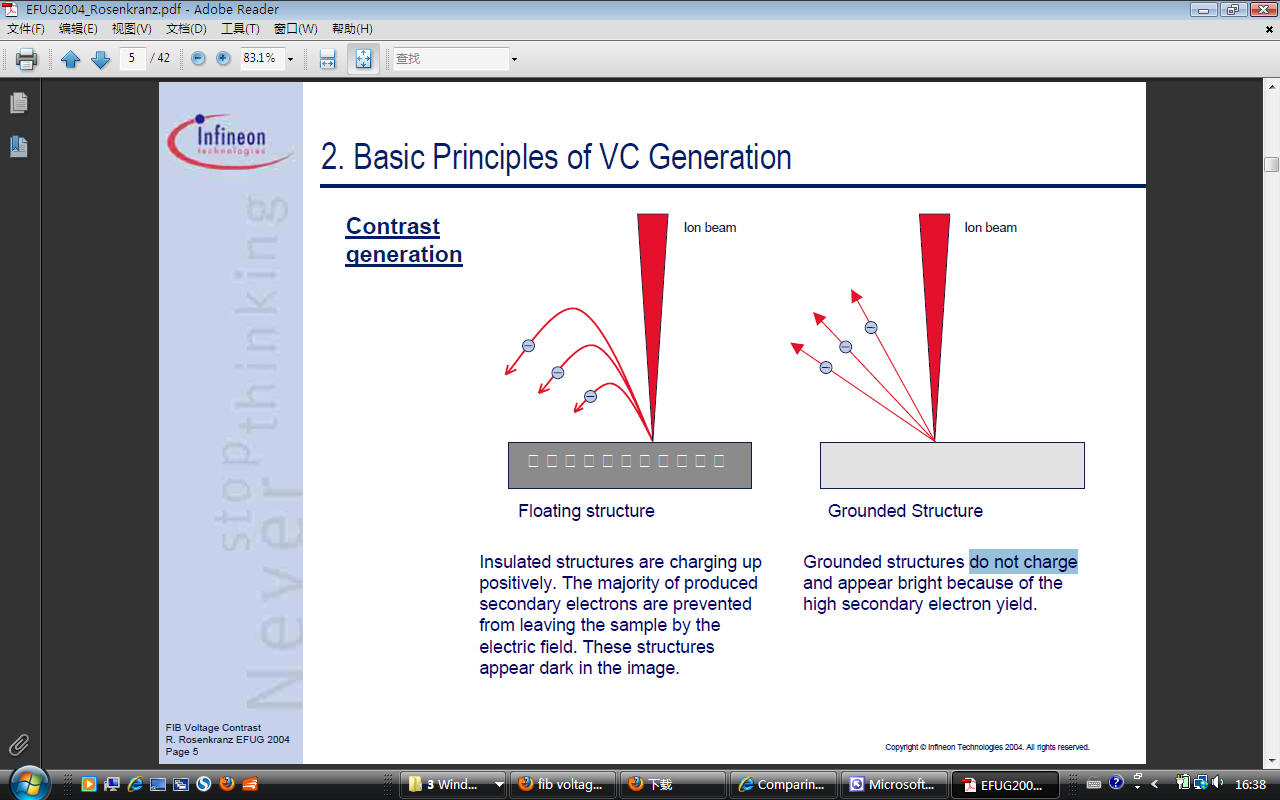
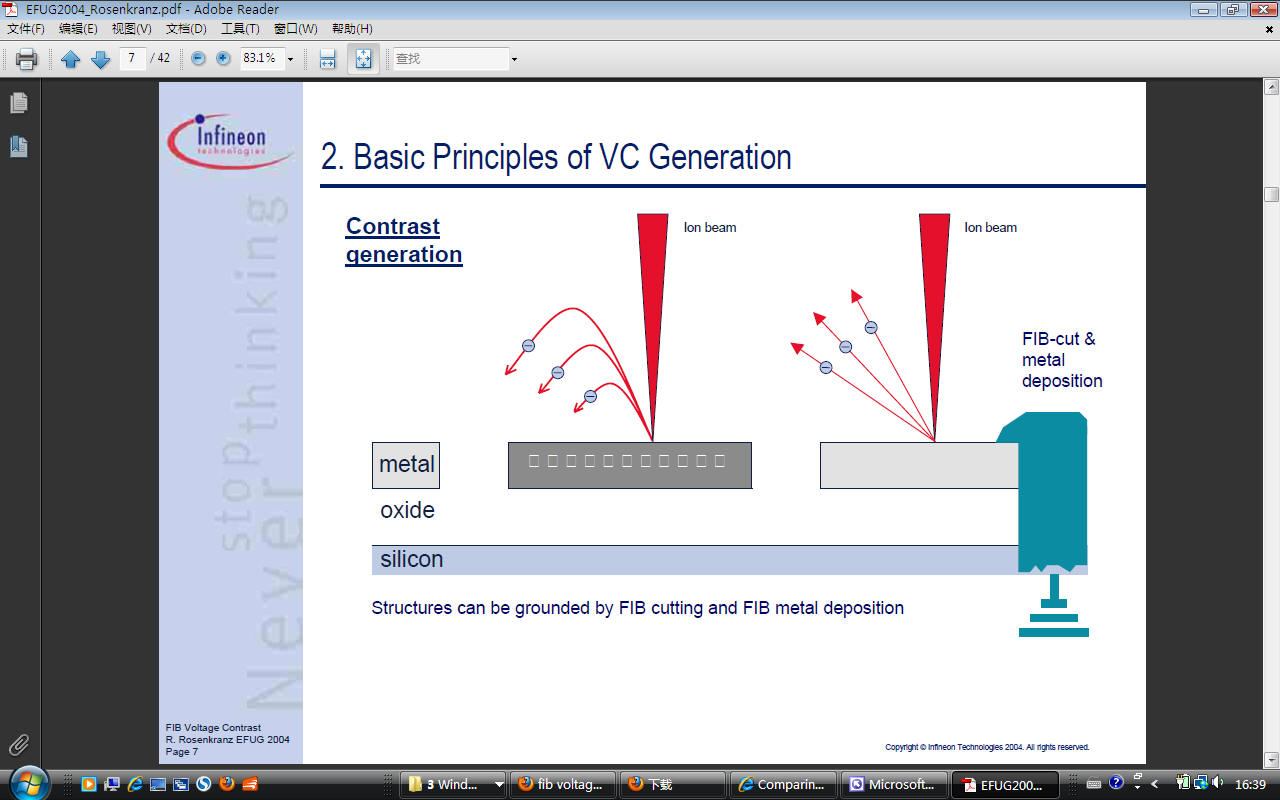
ser